Alzheimer’s Early Detection Test is revolutionizing how we approach cognitive health, providing a window into identifying individuals at risk of neurodegenerative diseases long before traditional symptoms emerge. Recent research conducted by a team at Mass General Brigham highlights the innovative use of olfactory tests as a potential method for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease and assessing cognitive impairment through a simple smell test. This groundbreaking study shows that such tests, which evaluate the ability to identify and remember various odors, can be conveniently conducted at home. By targeting the subtle loss of smell that often accompanies cognitive decline, researchers aim to create non-invasive and cost-effective tools that offer early Alzheimer’s diagnosis. These findings not only pave the way towards better preventive measures but also set the stage for enhanced research and treatment options in the realm of neurodegenerative diseases.
The exploration of Alzheimer’s Early Detection Test highlights emerging methodologies in recognizing early signs of cognitive decline. Known alternatively as olfactory assessment tools, these innovative tests evaluate a participant’s sense of smell to predict potential neurodegenerative conditions. This approach is significant as it enables early intervention for conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, allowing for a proactive rather than reactive healthcare strategy. Additionally, the evidence supporting the correlation between olfactory dysfunction and cognitive impairment signifies a potential new pathway in dementia research and management. As researchers continue to investigate these sensory assessments, the promise of better outcomes for patients with cognitive impairments becomes increasingly tangible.
Understanding Olfactory Tests for Early Alzheimer’s Detection
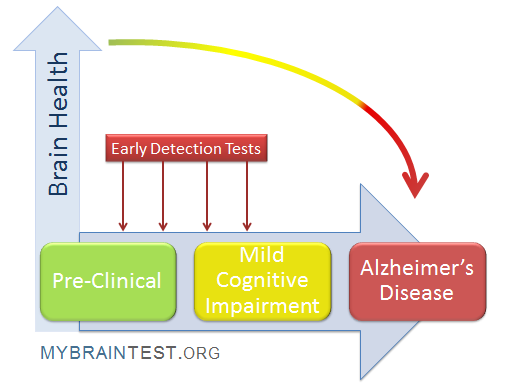
The development of olfactory tests marks a significant advancement in the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. By engaging participants to sniff various odor labels, researchers have effectively conceptualized a non-invasive method that can be conducted at home. These tests are crucial in identifying cognitive impairment, as studies indicate that older adults with such impairments struggle considerably with odor discrimination, identification, and memory compared to those with normal cognitive functions. This correlation underscores the potential of using smell tests as a reliable indicator for Alzheimer’s diagnosis.
As the research suggests, the implications of olfactory testing extend beyond just identifying Alzheimer’s risk; they potentially pave the way for ongoing monitoring of neurodegenerative diseases. With a user-friendly approach, the olfactory assessment could play a vital role in clinical settings. Early detection through these tests could allow for timely interventions, harnessing neuroprotective strategies that may delay or mitigate cognitive decline significantly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Alzheimer’s Early Detection Test and how does it work?
The Alzheimer’s Early Detection Test refers to innovative olfactory tests developed by researchers to assess cognitive impairment. This test evaluates an individual’s ability to identify and remember different odors, helping to identify those at risk of Alzheimer’s disease years before typical memory symptoms appear.
How does the olfactory test relate to Alzheimer’s diagnosis?
The olfactory test is closely related to Alzheimer’s diagnosis as it measures odor identification and memory. Research indicates that a decline in smell recognition can be an early indicator of cognitive impairment linked to Alzheimer’s, thus aiding in timely intervention.
Is the smell test effective in detecting early cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s patients?
Yes, the smell test is effective in detecting early cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s patients. Studies show that older adults with cognitive impairment score lower than cognitively normal individuals, indicating its potential as a screening tool.
Can the olfactory test be administered at home for Alzheimer’s early detection?
Absolutely! The olfactory test has been designed for at-home use, allowing individuals to assess their olfactory function conveniently. This approach makes early detection of cognitive decline more accessible.
Why is olfactory dysfunction significant in the context of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s?
Olfactory dysfunction is significant because a diminished sense of smell has been identified as an early warning sign for neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s. Recognizing this symptom can lead to earlier intervention strategies to mitigate disease progression.
What role does early detection play in Alzheimer’s disease management?
Early detection through tests like the olfactory assessment allows for timely interventions, which can improve the quality of life and potentially slow down the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. It helps in planning ahead for treatments and support systems.
Are there specific populations that benefit from the Alzheimer’s Early Detection Test?
Yes, both English and Spanish-speaking older adults with subjective cognitive complaints or mild cognitive impairment can benefit from the Alzheimer’s Early Detection Test. The tool is designed to be inclusive and effective across diverse linguistic groups.
What future developments can we expect for the Alzheimer’s Early Detection Test?
Future developments for the Alzheimer’s Early Detection Test may include integrating neuropsychological assessments and longitudinal studies to track cognitive decline over time, enhancing its predictive power for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Researchers from Mass General Brigham have developed an at-home olfactory test to detect Alzheimer’s risk early. |
| The test assesses odor discrimination, identification, and memory through sniffing odor labels on a card. |
| Older adults with cognitive impairment scored lower on the olfactory test compared to cognitively normal individuals. |
| The test showed effectiveness across English and Spanish speakers, indicating broad applicability. |
| Results suggest the olfactory test could predict cognitive decline and aid in early Alzheimer’s detection. |
Summary
The Alzheimer’s Early Detection Test represents a groundbreaking approach in identifying individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s disease long before clinical symptoms manifest. Researchers have demonstrated that simple olfactory tests performed at home can indicate cognitive impairments, laying the foundation for potential early interventions. By focusing on the sense of smell, this innovative method aims to provide a cost-effective, non-invasive solution that could transform Alzheimer’s research and treatment strategies.