Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent issue that requires immediate attention. Seniors, especially those aged 75 and older, face the highest risk of suicide among all age groups, yet many mental health resources for seniors remain scarce and hard to navigate. The intersection of loneliness in older adults and limited access to geriatric suicide risk support exacerbates this crisis, leading to a desperate need for tailored interventions. Online mental health support can be pivotal, but current resources often overlook the specialized needs of this vulnerable population. By addressing these gaps, society can create effective elderly suicide prevention strategies that not only save lives but also foster a healthier mental environment for our aging community.
The pressing need for elderly suicide intervention highlights a critical gap in mental health care aimed at seniors. As the geriatric population continues to grow, recognizing the extent of challenges like social isolation and despair becomes essential. In recent findings, researchers spotlight how older individuals struggle to find adequate support regarding suicide prevention, a situation worsened by the limited availability of tailored resources. To combat the alarming trend of increasing suicide rates among older adults, enhancing access to mental health interventions and online resources is imperative. This holistic approach can alleviate the burden of loneliness and elevate the mental well-being of our senior citizens.
Understanding the Geriatric Suicide Risk
The alarming statistic that adults aged 75 and older have the highest rates of suicide necessitates a deeper understanding of the geriatric suicide risk. This age group faces unique challenges, including health deterioration, social isolation, and a higher likelihood of experiencing bereavement, all of which can contribute to feelings of hopelessness. Additionally, older adults may not openly express their struggles, making it essential for caregivers and loved ones to recognize subtle signs of distress. Community awareness and education on these risks can be pivotal in identifying at-risk seniors and guiding them to appropriate mental health resources.
Moreover, older adults often battle misconceptions regarding mental health, which can deter them from seeking help. Traditional avenues of mental health support might not resonate with them, leading to a reliance on outdated ideas surrounding mental well-being. By tailoring approaches specifically aimed at this demographic, such as incorporating familiar communication methods or engaging activities, we can significantly enhance their willingness to reach out for assistance. Understanding the geriatric suicide risk is imperative for developing effective interventions that resonate with the elderly.
Addressing Loneliness in Older Adults
Loneliness is a pervasive issue among older adults and has significant implications for their mental health. Studies have consistently shown that social isolation can heighten the risk of depression and anxiety, contributing to suicidal thoughts or attempts. Implementing effective strategies to combat loneliness can drastically improve the emotional and psychological well-being of seniors. Community programs, peer support groups, and social events can create opportunities for older adults to connect, share experiences, and foster relationships that can alleviate feelings of isolation.
Furthermore, technology can play a crucial role in reducing loneliness among older adults. Many seniors are increasingly becoming tech-savvy, utilizing online platforms to stay in touch with friends, family, and the broader community. By promoting digital literacy and providing access to online mental health support, we can empower older adults to seek companionship and professional help when needed. Investing in training programs that teach seniors how to use social media and communication tools can further bridge the gap of loneliness while offering a means to access mental health resources.
Mental Health Resources for Seniors
Despite the growing awareness of mental health issues among older adults, there remains a stark lack of accessible mental health resources specifically tailored for this population. Many national organizations focus predominantly on younger demographics, overlooking the unique needs of seniors. To effectively support mental well-being, resources should be designed with older adults in mind, considering factors such as cognitive impairments, physical limitations, and varying levels of comfort with technology. Making mental health resources more visible and accessible is a crucial step towards preventing elderly suicide.
In addition, promoting collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, community organizations, and tech developers can lead to the creation of more effective mental health resources for seniors. By fostering partnerships that address this demographic’s needs, we can ensure that essential services are not only available but also relatable and user-friendly. Increasing awareness about mental health resources for seniors can encourage those in need to seek help and reduce the stigma associated with accessing mental health services.
Online Mental Health Support for Seniors
The rise of technology has opened new avenues for mental health support through online platforms, offering alternatives that can be particularly beneficial for older adults. Many seniors may find it easier to reach out for help via online channels rather than traditional face-to-face interactions. Virtual counseling sessions, support groups, and mental health hotlines tailored for seniors can significantly increase accessibility, particularly for those who have mobility challenges or live in rural areas where resources may be limited.
Despite the benefits, there are still hurdles in ensuring that online mental health support services are effectively marketed and accessible to older adults. Communication strategies must resonate with seniors, utilizing familiar channels and language to bridge the digital divide. By highlighting resources specifically designed for older adults, we can encourage them to take advantage of available online mental health support, ultimately promoting better mental health outcomes and reducing the risk of suicidal thoughts.
The Importance of Targeted Suicide Prevention Campaigns
As highlighted by recent research, there is an urgent need for targeted suicide prevention campaigns that address the unique experiences of older adults. General public-focused campaigns may not resonate with this demographic, leading to a lack of engagement with vital resources. Tailored initiatives that speak directly to the issues seniors face, such as isolation, grief, and mental health stigma, can drive engagement and create a supportive environment encouraging older adults to seek help.
These campaigns should leverage various platforms, including social media, community notice boards, and senior centers, to ensure they reach older adults effectively. Furthermore, collaborative efforts encompassing healthcare systems and community organizations can amplify the message and foster a culture of awareness and support. By prioritizing targeted suicide prevention campaigns, we can help bridge the gap for older adults in accessing necessary mental health resources and ultimately save lives.
Innovating Mental Health Solutions for the Elderly
Innovation in mental health solutions for the elderly is crucial in addressing the growing crisis of elderly suicide. This involves not only creating more accessible resources but also reimagining how these resources are delivered. Integrating technology, such as teletherapy and digital mental health apps, can revolutionize how older adults receive support. Such innovations can provide real-time assistance, making mental health care more responsive to the immediate needs of older adults who may be in crisis.
Additionally, mental health solutions must be culturally competent and respectful of the diverse experiences of older adults. Collaborative development involving seniors in the design phase can ensure that the developed solutions resonate well with them. Regular feedback from older adults can foster continuous improvement and adaptation of protocols. By innovating mental health solutions for the elderly, we can create a more supportive framework that addresses the nuances of geriatric mental health challenges.
Funding and Research for Late-Life Suicide Prevention
An essential factor in advancing suicide prevention efforts for older adults is increasing funding and research focused specifically on late-life mental health challenges. Many existing research initiatives primarily target younger populations, which results in a lack of tailored interventions and resources accessible to seniors. By channeling more resources towards exploring the unique triggers and risk factors of geriatric suicide, we can develop more effective prevention strategies that address the core issues at play within this demographic.
Furthermore, increasing financial support for elder mental health initiatives can help establish community-based programs specifically designed for older adults. This includes funding for training health professionals in geriatric mental health, developing outreach programs, and creating supportive environments that foster social connections among seniors. Greater investment in research and funding can lead to innovative solutions and widespread reforms that directly benefit older adults at risk of suicide.
Community Engagement and Suicide Prevention
Community engagement plays a pivotal role in suicide prevention among older adults. Strong community ties can alleviate feelings of loneliness and isolation, significantly reducing the risk of suicidal thoughts. Local initiatives aimed at creating more inclusive environments for seniors can encourage participation in community activities and foster supportive relationships. Community leaders should work to create opportunities for interaction, such as social gatherings, workshops, or volunteer programs that specifically cater to older adults.
Moreover, training volunteers and community members to recognize signs of distress and respond appropriately can empower those around at-risk seniors to provide essential support. Programs that promote mental health awareness and education in community centers can help destigmatize mental health issues, encouraging older adults to seek help. Effective community engagement, when combined with direct resources and support, can build resilience among older adults, promoting mental wellness in this vulnerable population.
The Role of Family in Elderly Suicide Prevention
Family members play a crucial role in the suicide prevention efforts for older adults. Often, they are the first line of defense in recognizing changes in behavior, mood, and overall mental health in their aging relatives. Open lines of communication within families can help ensure that seniors feel supported and valued, potentially reducing their feelings of isolation and helplessness. Educating families on the signs of mental distress in older adults can empower them to seek help earlier and more effectively.
Additionally, families can advocate for their elderly relatives by seeking out appropriate mental health resources and encouraging engagement in community programs. By fostering an inclusive family environment that values mental health, families can contribute significantly to reducing the stigma surrounding the topic. Such supportive structures can play a vital role in deterring suicidal thoughts among older adults, illustrating the powerful impact of family involvement in mental health care.
The Future of Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
As we look forward, the future of suicide prevention for older adults hinges upon a comprehensive and empathetic approach to mental health care. Innovative strategies and community-based resources must evolve to meet the distinct needs of seniors. This includes advocating for integration of mental health services within broader healthcare frameworks, ensuring that older adults can receive holistic and accessible support.
Moreover, ongoing evaluation and adaptation of suicide prevention programs are essential to ensure their effectiveness. Engaging older adults as partners in the development and implementation of these strategies will not only enhance their efficacy but also empower seniors within their communities. A multifaceted future for elderly suicide prevention that embraces innovation, education, and collaboration could pave the way for safer mental health outcomes for older adults, decreasing vulnerability and fostering resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective strategies for elderly suicide prevention?
Effective elderly suicide prevention strategies include increasing awareness of mental health resources for seniors, promoting social connections to reduce loneliness in older adults, and ensuring easy access to geriatric suicide risk assessments and supportive services. Creating online mental health support systems tailored for older adults can also play a vital role.
How can loneliness in older adults impact geriatric suicide risk?
Loneliness in older adults significantly contributes to geriatric suicide risk by exacerbating mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety. Addressing social isolation through community outreach programs and promoting connections can help mitigate these risks.
Where can I find online mental health support for older adults?
Online mental health support for older adults can be found through various resources, including national mental health organizations, local community services, and dedicated hotlines aimed at elderly suicide prevention. Many websites now cater specifically to the unique needs of seniors, providing tailored information and support.
What resources are available for mental health issues in older adults?
Mental health resources for seniors include hotlines, counseling services, and community mental health programs designed specifically for older adults. Many organizations also offer online platforms that provide information, support groups, and links to geriatric experts to address the mental health needs of this age group.
How does the healthcare system need to change for elderly suicide prevention?
The healthcare system must prioritize elderly suicide prevention by incorporating targeted campaigns that address the unique mental health needs of older adults. This includes better training for healthcare professionals in recognizing geriatric suicide risk, increasing funding for research focused on late-life mental health, and improving access to mental health resources for seniors.
What role do family members play in preventing elderly suicide?
Family members play a crucial role in preventing elderly suicide by providing emotional support and recognizing signs of mental distress in their loved ones. Encouraging open communication about feelings and seeking professional help when needed are key steps that families can take to support older adults struggling with suicidal thoughts.
Are there any specific warning signs for suicide risk in older adults?
Yes, warning signs for suicide risk in older adults include expressing feelings of hopelessness, withdrawal from social activities, changes in mood or behavior, and giving away personal belongings. Awareness of these signs can help caregivers and family members intervene early and seek appropriate mental health resources.
Why is there a lack of suicide prevention resources targeting older adults?
There is a lack of suicide prevention resources targeting older adults due to systemic biases that often overlook the mental health needs of seniors, coupled with underrepresentation in research initiatives. This imbalance emphasizes the need for organizations to develop comprehensive support networks specifically designed for the elderly population.
What initiatives are being proposed to improve elderly suicide prevention?
Proposed initiatives to improve elderly suicide prevention include developing accessible online mental health support tailored for seniors, increasing funding for research on geriatric suicide risk, and implementing targeted public awareness campaigns aimed at highlighting and addressing the unique healthcare needs of older adults.
How can community programs help with elderly suicide prevention?
Community programs can assist with elderly suicide prevention by providing social activities that reduce loneliness, offering workshops on mental health awareness, and facilitating access to mental health resources for seniors. Such initiatives create supportive networks that help older adults feel connected and cared for.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
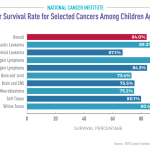
| High Suicide Risk in Older Adults | Adults aged 75 and older have the highest suicide rates, approximately 20.3 per 100,000. |
| Lack of Resources | Existing national suicide prevention organizations do not sufficiently target older adults. |
| Imbalance in Online Resources | Older adults struggle to find accessible online resources for suicide prevention. |
| Consequences of Isolation | Social isolation and loneliness contribute to the higher suicide rates in older adults. |
| Need for Targeted Campaigns | There is a pressing need for suicide prevention campaigns tailored specifically to the needs of older adults. |
| Funding and Research | Increased funding for research and tailored programming for late-life suicide prevention is essential. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue that requires immediate attention and action. Despite being the age group with the highest suicide rates, individuals aged 75 and older often lack access to the necessary resources and support systems. Research highlights a significant imbalance in suicide prevention efforts, revealing that these resources are not adequately tailored for older adults, leading to an underrepresentation of their unique healthcare needs. Addressing this gap through targeted campaigns and increased funding for research is essential in ensuring that older adults receive the support they need to prevent suicide.