Prion disease treatment has emerged as a beacon of hope for those suffering from these devastating neurodegenerative disorders. With conditions such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia, which are caused by misfolded proteins, the quest for effective therapies has taken on urgent significance. Recent breakthroughs in gene-editing therapy may pave the way for a cure, as researchers have demonstrated the ability to significantly reduce prion protein levels in animal models, extending their lifespans by significant margins. The promise of these therapeutic advancements marks a pivotal shift in the landscape of prion disease research, inviting anticipation for human trials that could change lives. As scientists like Sonia Vallabh and her husband Eric Minikel lead efforts in this crucial field, the prospect of treating these rare yet fatal conditions becomes increasingly tangible.
The advancement in treatment options for prion-related disorders reflects a growing understanding of these rare yet severe conditions, often referred to collectively as prion diseases. Characterized by the accumulation of aberrantly folded proteins in the brain, ailments such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease pose considerable challenges to both patients and researchers. Groundbreaking developments in genetic manipulation techniques, like those seen in gene-editing therapies, offer fresh perspectives on potential remedies. With pioneering work currently underway, scientists are striving to translate these lab findings into viable treatment options for affected individuals suffering from conditions including fatal familial insomnia. As the scientific community navigates the path toward clinical trials, the hope for effective interventions continues to build.
Understanding Prion Disease and Its Impact
Prion diseases, often referred to as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, encompass a group of rare, progressive neurodegenerative disorders characterized by the misfolding of prion proteins in the brain. These conditions result in severe brain damage and significant cognitive decline, leading to devastating outcomes for patients and their families. Among the most notorious prion diseases is Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), which manifests rapidly and is invariably fatal. Other forms, such as fatal familial insomnia (FFI), not only affect sleep patterns but also lead to complex symptoms of dementia and severe neurological disruption.
The global implications of prion diseases extend beyond individual patients, impacting healthcare systems and necessitating extensive research and resources. With approximately 15% of prion disease cases linked to inherited mutations in the prion protein gene, genetic counseling and awareness are paramount. Sporadic cases, which account for a staggering 85% of diagnoses, highlight the unpredictable nature of these conditions. Thus, understanding prion diseases is crucial for both patient care and the advancement of scientific research aimed at curtailing their impact.
Promising Advances in Prion Disease Treatment
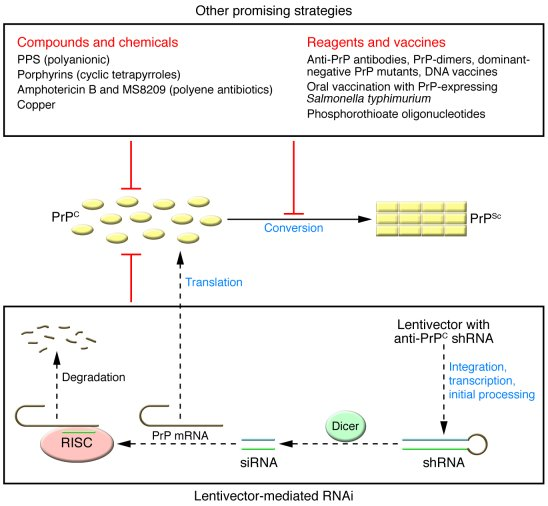
Recent research breakthroughs have ignited hope for prion disease treatment, particularly through innovative gene-editing therapy. Scientists led by David Liu at the Broad Institute successfully utilized a novel base editing technique that targets the specific mutations within the prion protein gene. This method has shown promise in laboratory mice, resulting in a significant 52% extension of lifespan by drastically reducing the production of harmful prion proteins. Such therapeutic advancements pave the way for future clinical applications, raising anticipation in the scientific community about potential human trials.
While the journey to human trials remains complex and lengthy, the groundwork laid by researchers signifies a monumental step toward effective treatments for devastating conditions like CJD and FFI. This is particularly critical given the psychological and physical toll on patients and their families. The collaboration between patient-scientists and professional researchers enhances motivation and focus on delivering impactful solutions. As the field moves forward, the integration of advanced therapeutic techniques and thorough scientific inquiry becomes vital in the quest for viable prion disease treatment.
The Personal Motivations Behind Prion Disease Research
The intersection of personal experience and scientific inquiry is vividly illustrated in the work of Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel, both of whom are directly impacted by prion disease. Vallabh’s positive test for the FFI variant of prion disease, particularly after losing her mother to the same condition, shapes her research aspirations. This poignant personal connection fuels their laboratory’s commitment to unraveling the complexities of prion diseases, providing an extraordinary motivation for their research team as they strive toward breakthroughs that could save lives.
In a field often perceived as abstract, the involvement of patient-scientists introduces a compelling narrative of hope and urgency around prion disease research. Vallabh and Minikel’s dedication embodies the essence of translational medicine, where personal experiences drive the desire to innovate effective therapies. The collaborative nature of their work not only enriches the scientific dialogue but also inspires other researchers, creating an environment where personal connections may lead to meaningful advancements and therapeutic solutions.
Gene-Editing Therapy: A Game Changer for Prion Diseases
Gene-editing therapy has emerged as a transformative potential in the treatment of prion diseases, offering revolutionary approaches to tackle their genetic underpinnings. By employing sophisticated techniques such as CRISPR and base editing, researchers can now precisely target and modify the genes responsible for producing misfolded prion proteins. This technical advancement could dramatically alter the treatment landscape for conditions like CJD and FFI, which currently have no effective cures. The ability to correct genetic mutations at their source stands as a hopeful prospect in the urgent pursuit of therapeutics.
The implications of successful gene-editing therapy are profound. Not only could these treatments drastically improve patient outcomes, but they also mark a significant leap forward in understanding the fundamental mechanisms behind prion diseases. The ongoing research, which has shown promising results in animal models, sows the seeds for future human trials that could bring these therapies into clinical settings. As scientists continue to refine these techniques, the potential for impactful clinical applications grows, promising a new dawn in the fight against fatal familial insomnia and other devastating prion disorders.
Challenges Ahead: From Laboratory to Clinical Trials
Transforming laboratory advancements into viable clinical therapies is fraught with challenges, especially in the context of prion disease. Although the promising results from recent gene-editing research provide a beacon of hope, the pathway to human trials is complex and requires navigating numerous regulatory, ethical, and logistical hurdles. Factors such as ensuring the safety of gene-editing techniques and addressing potential risks associated with prion proteins underscore the need for meticulous groundwork before transitioning into human subjects.
Moreover, researchers must prioritize refining their methodologies to enhance the efficacy and specificity of gene-editing therapies. As demonstrated in recent studies, optimizing vectors for delivery and minimizing unintended consequences are key areas of focus. These advancements are critical not only for prion diseases but also for the broader context of gene therapy as a whole. Collaborative efforts between laboratories, institutions, and regulatory bodies will be essential in overcoming these barriers, ultimately heralding a new era of hope for patients and their families.
The Role of Collaborative Research in Prion Disease Solutions
Collaborative research plays a pivotal role in addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by prion diseases. Expert practitioners from various fields, including neurology, genetics, and therapeutic development, come together to share insights, data, and techniques that can drive innovation forward. This interdisciplinary approach has been critical in the advancement of gene-editing therapy, as evidenced by the ongoing partnership between Vallabh, Minikel, and Liu’s team at the Broad Institute. Their joint efforts exemplify how diverse expertise can lead to groundbreaking discoveries.
The synergy in collaborative environments accelerates progress while fostering a culture of shared determination and motivation. As researchers witness the tangible impact of their efforts on individuals personally affected by prion diseases, the urgency to innovate intensifies. Such collective endeavors amplify the likelihood of translating exploratory research into practical therapies, signifying a crucial step towards addressing the desperate need for effective treatment solutions for patients suffering from prion disorders.
Safety Considerations in Prion Disease Gene Therapy
When considering gene therapy for prion diseases, safety remains a paramount concern for both researchers and subject participants. Given the contagious nature of prion proteins and the severe consequences of prion disease, strategies must be employed to mitigate any adverse effects during the therapeutic process. Researchers must thoroughly evaluate the potential risks associated with using vectors, which deliver gene-editing tools to target cells, as well as monitor the long-term effects that these interventions may have on neural tissues.
The lessons learned from past research, including accidental exposures that led to fatalities, underscore the necessity for rigorous safety protocols in prion disease studies. Continuous improvement in vector engineering alongside robust preclinical testing is essential to ensure that therapeutic advancements can be safely transitioned into human applications. As the field evolves, prioritizing safety will be vital not only for gaining regulatory approval but also for fostering public trust in emerging gene-editing therapies.
Implications of Prion Disease Research on Public Health
The implications of advancements in prion disease research reach far beyond individual patients and touch on broader public health concerns. Improved understanding and potential treatment options for these rare but deadly diseases can mitigate the ripple effects on families, caregivers, and healthcare systems. As researchers develop innovative therapies, they also contribute to the larger narrative of neurodegenerative disease management, encouraging preventive measures, genetic counseling, and increased awareness surrounding prion diseases.
Moreover, heightened public awareness can translate into greater funding for research efforts aimed at prion diseases, amplifying the collective fight against these conditions. As we continue to explore and innovate in the field of genetics and molecular therapies, the societal impact of scientific endeavors becomes increasingly significant. The ongoing collaboration between clinical practitioners, researchers, and affected individuals will be crucial in steering the future direction of public health strategies related to prion disease management.
The Future of Prion Disease Treatment Innovations
Looking ahead, the future of prion disease treatment holds substantial promise, thanks to the ongoing research and innovative breakthroughs emerging from the field of genetics and biotechnology. The fruits of collaborative efforts in laboratories around the globe could yield new therapeutic protocols that harness the powerful capabilities of gene-editing techniques. As the field moves closer toward human trials, it raises new questions about the potential of these therapies to not only treat but possibly cure conditions historically deemed untreatable.
With a concerted focus on developing safe and effective treatment strategies, the potential benefits of prion disease therapies may extend beyond the immediate patient population to influence a broader understanding of protein misfolding disorders. As researchers remain vigilant in their quest for answers and breakthroughs in therapeutic advancements, the future remains optimistic. This scientific revolution heralds not just hope for those affected by prion diseases but exemplifies the unyielding human spirit in the face of formidable health challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the latest advancement in prion disease treatment related to gene-editing therapy?
Recent research highlights a promising gene-editing therapy that targets the genetic basis of prion diseases. Scientists at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have developed a method to alter a single base in the prion protein gene, reducing harmful protein levels in laboratory mice by 50%. This breakthrough indicates significant potential for developing effective treatments for various prion diseases, including Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
Are there any ongoing human trials for prion disease treatment?
Human trials for prion disease treatment are still several years away. Current research has shown encouraging results in animal models, specifically using gene-editing techniques, but more development is required before testing in humans can commence. Researchers caution that several milestones must be achieved to ensure safety and efficacy.
How does gene-editing therapy work for treating fatal familial insomnia and other prion diseases?
Gene-editing therapy aims to correct the mutations responsible for prion diseases like fatal familial insomnia. By utilizing a base editing technique, researchers can modify specific genetic sequences associated with the dysfunctional prion protein. This alteration helps to decrease the production of toxic proteins in the brain, potentially halting disease progression and extending lifespan in affected models.
What are the challenges in developing effective treatments for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease?
Developing effective treatments for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease involves numerous challenges, including the complex nature of prion proteins and their ability to misfold. Additionally, safety concerns surrounding the viral vectors used in gene-editing therapy must be addressed to prevent adverse effects. The translational process from laboratory findings to human applications is lengthy and requires extensive testing and validation.
What potential does therapeutic advancements in prion disease treatment hold for the future?
Therapeutic advancements in prion disease treatments offer hope for not only extending lifespan but also providing effective disease management for individuals affected by conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia. As researchers continue to refine gene-editing technologies and conduct rigorous studies, the potential for breakthroughs that could enhance patient outcomes is significant.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Advances | Promising gene-editing therapy shows potential to treat prion disease by reducing misfolded proteins. |
| Personal Connection | Sonia Vallabh, a patient scientist, drives research efforts due to her own diagnosis of fatal familial insomnia. |
| Base Editing Technology | Technique reduces toxic protein levels in mouse brains, extending lifespan by 52%. |
| Milestones Ahead | Several steps remain before human trials can occur, indicating a lengthy process. |
| Safety Improvements | Modifications to reduce viral vector-related side effects while enhancing efficacy. |
| Collaborative Efforts | Involvement of various experts fostering a motivated environment for breakthrough research. |
Summary
Prion disease treatment is advancing as innovative research uncovers potential gene-editing therapies. With scientists like Sonia Vallabh directly affected by the affliction, there’s an immense drive towards finding solutions. Recent findings indicate that editing a single genetic component can significantly diminish harmful proteins in the brain, marking significant progress towards a potential treatment. Despite remaining challenges before human clinical trials, the work’s promising nature instills hope for those impacted by these devastating disorders.