Bile acid imbalance has emerged as a significant factor in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Recent studies reveal that dysregulation of bile acids—critical components produced by the liver for fat digestion—not only disrupts digestive health but also contributes to severe liver diseases, including liver cancer. Researchers have pinpointed a key molecular switch that controls bile acid production, highlighting new avenues for liver cancer treatment and intervention. Furthermore, this imbalance initiates a cascade of liver inflammation and injury, demonstrating the intricate link between bile acids and health. Understanding pathways such as the YAP FXR pathway offers hope for improving liver disease research and developing effective therapies against liver cancer.
The disturbance in bile acid homeostasis plays a crucial role in the onset of liver malignancies, with a notable emphasis on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids, integral for fat digestion, serve not just as digestive agents but also influence metabolic processes profoundly. Exploring the regulatory mechanisms of these acids has unveiled potential strategies for therapeutic interventions in liver cancer treatment. In particular, the signaling pathways involved, such as the Hippo/YAP pathway, represent a vital area of investigation in liver disease research. With increased awareness of how bile acid imbalances affect liver health, researchers are better equipped to address these challenges and enhance patient outcomes.
Understanding Bile Acid Imbalance and Its Role in Liver Cancer
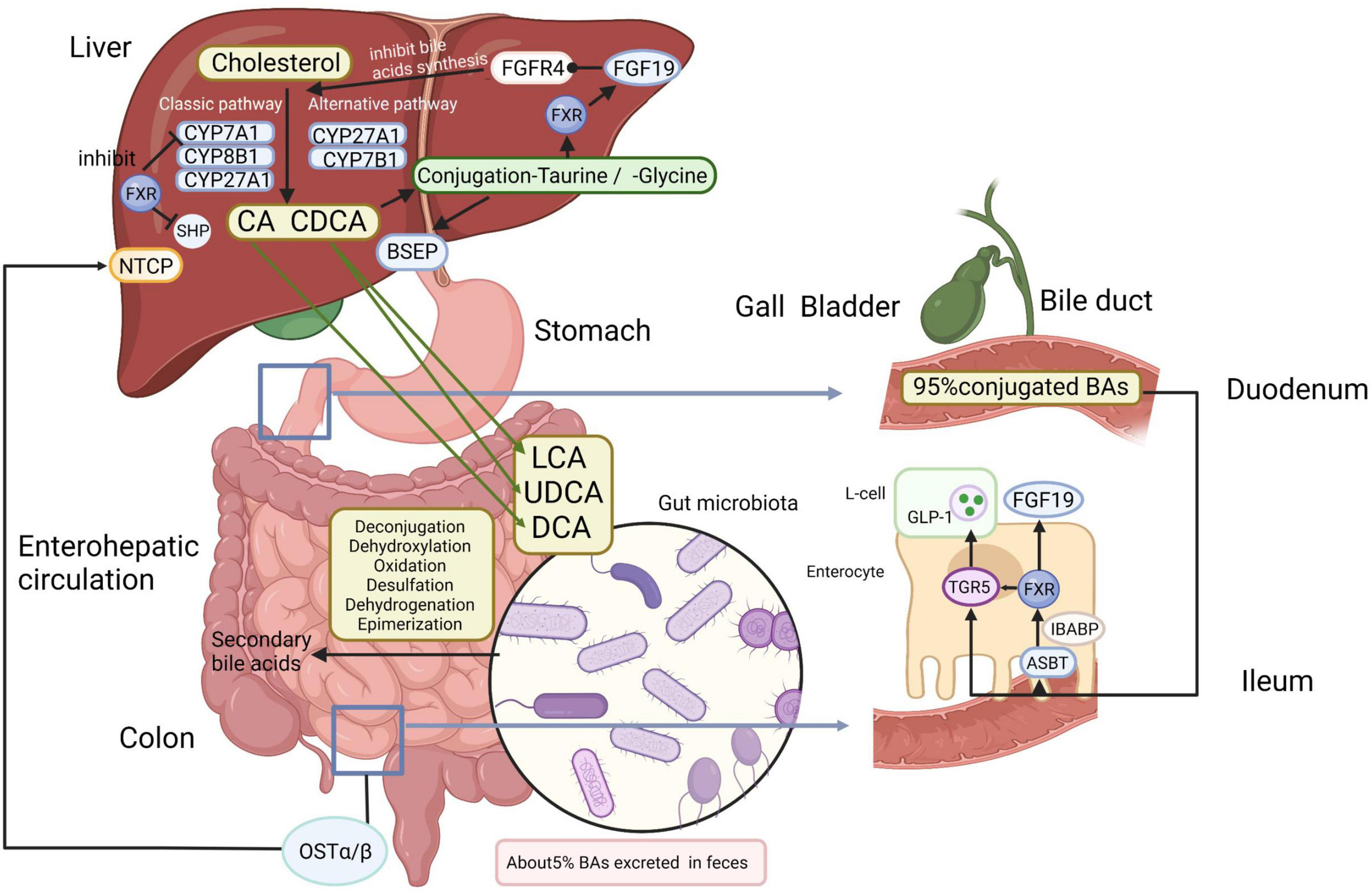
The liver is a vital organ responsible for various life-sustaining functions, one of which includes the production of bile acids. These compounds are essential for the digestion and absorption of fats in our diet. However, an imbalance in bile acid levels has been increasingly implicated in several liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. Recent research has shed light on the mechanisms underlying this imbalance, revealing that disruptions can trigger liver injury and significantly contribute to the development of cancerous lesions.
When bile acids are produced in excess due to factors such as impaired regulation of signaling pathways, they accumulate in the liver, leading to toxic effects. This abnormal accumulation prompts a cascade of inflammation and fibrosis, setting the stage for malignant transformations. Understanding the intricate relationship between bile acid metabolism and liver cancer is critical for developing effective treatments. By targeting specific pathways involved, such as the YAP FXR pathway, researchers hope to restore normal bile acid homeostasis, thereby mitigating the risk of liver cancer.
The YAP FXR Pathway and Its Implications for Liver Disease Research
Research into the YAP FXR pathway reveals a significant connection between cell signaling and liver cancer development. YAP, or Yes-associated protein, is known for its role in cell growth regulation. Interestingly, this study highlights a dual function of YAP, which not only promotes tumor formation but also represses the activity of FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) — a key regulator of bile acid metabolism. When YAP inhibits FXR function, it disrupts bile acid homeostasis, leading to excessive bile acid production and subsequent liver damage.
The implications of these findings extend beyond understanding liver cancer; they pave the way for innovative therapeutic approaches. By targeting the YAP FXR pathway, potential pharmacological solutions could be developed to enhance FXR function or facilitate bile acid excretion. This strategy may not only reduce liver damage due to excess bile acids but also stall cancer progression effectively. As researchers delve deeper into the cellular mechanisms of liver diseases, the insights gained here could lead to groundbreaking advancements in liver cancer treatment.
Bile Acids and Health: Beyond Digestion
Bile acids serve crucial roles beyond their well-known function in fat digestion. Recent studies highlight their importance as signaling molecules that influence various metabolic processes and maintain overall liver health. The balance of bile acids is necessary not just for proper digestion, but also for preventing liver diseases. Imbalances can lead to conditions ranging from steatosis to severe liver damage and even cancer, necessitating a broader understanding of bile acids in health and disease.
Research continues to uncover the mechanism by which bile acids regulate metabolic pathways and their impact on diseases such as diabetes and obesity. In particular, the interplay between bile acids and nuclear receptors like FXR underscores their importance in maintaining metabolic equilibrium. By elucidating these relationships, healthcare professionals can develop strategies that leverage bile acid signaling to combat liver diseases and related health issues effectively.
Innovative Approaches in Liver Cancer Treatment Strategies
As highlighted in recent findings, innovative approaches in liver cancer treatment focus on targeting the underlying metabolic dysregulations associated with bile acid imbalance. The discovery of the YAP FXR pathway not only enhances our understanding of liver cancer mechanisms but also opens the door to novel therapeutic strategies. By developing drugs that can activate FXR or inhibit YAP’s repressive effects, researchers aim to correct the bile acid imbalance, potentially halting tumor progression.
Current liver cancer treatments often fall short of success due to the complex nature of the diseases. However, incorporating knowledge of bile acid metabolism into treatment protocols could shift the paradigm toward more personalized medicine. Ongoing research in liver disease underscores the importance of understanding individual metabolic responses, fostering the development of targeted therapies that could lead to improved outcomes for patients battling liver cancer.
Promoting Bile Acid Excretion: A Key to Halting Liver Damage
One promising avenue in reversing liver damage linked to bile acid imbalance involves enhancing bile acid excretion. The research findings suggest that promoting the function of bile acid export proteins, such as BSEP (Bile Salt Export Pump), can help alleviate the toxic effects of excess bile acids. This approach could alleviate liver fibrosis and inflammation, subsequently hindering the progression to hepatocellular carcinoma.
Investigating the molecular mechanisms that govern bile acid excretion is critical for developing effective therapies. By targeting the pathways that regulate bile transport and reinforcing the body’s natural ability to eliminate excess bile acids, researchers aim to prevent the detrimental impacts on liver health. This strategy represents a forward-thinking approach in liver disease management and highlights the need for continued research in bile acids and liver cancer.
The Importance of Cell Signaling in Liver Cancer Research
Understanding the intricate web of cell signaling pathways is paramount in liver cancer research. These pathways govern various cellular processes, including growth, survival, and metabolism, all of which can be dysregulated in cancer. The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway is of particular interest, as it plays a crucial role in liver size regulation and tissue homeostasis. Disruption in this pathway not only contributes to tumorigenesis but also impacts bile acid metabolism, establishing a direct link between cellular signaling and liver cancer.
By focusing on the molecular mechanisms behind cell signaling, researchers are uncovering critical insights into the pathophysiology of liver diseases. Enhanced understanding of these interactions can lead to the identification of biomarkers that may aid in early diagnosis and treatment. Furthermore, this foundational knowledge is essential for the development of targeted therapies that can specifically modulate these pathways, ultimately improving patient outcomes in liver cancer.
Future Directions in Liver Disease and Cancer Prevention Research
As liver disease and cancer continue to pose significant public health challenges, future research must prioritize understanding the role of bile acid imbalance in these conditions. With advancements in genomic and molecular biology techniques, researchers are now equipped to explore the complex interactions between dietary components, metabolic processes, and their implications for liver health. These investigations will be pivotal in developing preventive measures against liver cancer and related disorders.
Moreover, given the rising prevalence of liver diseases worldwide, there is a pressing need for public health initiatives that promote awareness of the link between bile acids and liver health. Insights from ongoing research can inform dietary guidelines aimed at reducing the risk of liver cancer through proper regulation of bile acid metabolism. By coupling scientific discovery with community education, we can take significant steps toward lowering liver disease incidence and improving overall health outcomes.
Clinical Implications of Bile Acid Research for Liver Cancer Patients
The clinical implications of bile acid research are profound for patients diagnosed with liver cancer. Understanding bile acid metabolism not only provides insights into disease progression but also informs treatment decisions. For instance, patients with high levels of bile acids may benefit from interventions aimed at restoring balance through pharmacological therapies or lifestyle modifications, emphasizing the need for personalized approaches based on individual metabolic profiles.
Moreover, as research continues to validate the role of bile acids in liver cancer treatment, there may be a shift toward incorporating bile acid modulation strategies into standard care protocols. Clinicians could leverage these findings to offer more effective treatment options that not only address cancer but also aim to prevent liver damage caused by bile acid dysregulation, ensuring a comprehensive approach to patient health.
Addressing Liver Health Through Integrated Research Approaches
A holistic approach to liver health requires integrated research efforts that bridge various scientific disciplines. As researchers from developmental biology, oncology, and metabolic studies come together, the potential to uncover novel insights into liver diseases increases significantly. Investigating the interplay between bile acids, metabolism, and cancer pathways underscores the need for a collaborative approach to address the myriad challenges posed by liver disease.
By fostering interdisciplinary collaborations, researchers are better equipped to tackle complex issues surrounding liver cancer. Integrating findings across studies will facilitate a deeper understanding of the role that bile acid imbalance plays in disease development and create pathways to innovative treatments. The ultimate goal remains to enhance liver health and reduce the burden of liver cancer through informed scientific exploration and collaborative problem-solving.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between bile acid imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile acid imbalance is increasingly recognized as a contributing factor in liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). When bile acids, which are produced by the liver to aid fat digestion, become imbalanced, they can lead to liver injury and inflammation. This disruption is linked to the activation of the YAP FXR pathway, where YAP hinders the function of the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), leading to overproduction of bile acids. This accumulation can result in fibrosis and ultimately progresses to liver cancer.
How does the YAP FXR pathway relate to bile acid metabolism and liver cancer treatment?
The YAP FXR pathway plays a crucial role in bile acid metabolism. YAP, when activated, represses the FXR, a key bile acid sensor, leading to an imbalance. This overproduction of bile acids can cause liver damage and promote hepatocellular carcinoma. Researchers suggest that targeting this pathway—by enhancing FXR function or blocking YAP’s repressive effects—might offer new liver cancer treatment options that reduce damage and hinder cancer progression.
What are the implications of bile acids and health in liver disease research?
Bile acids are not just important for digestion; they also serve as signaling molecules that influence metabolic processes. In liver disease research, understanding how bile acids interact with cellular signaling pathways like YAP FXR can help identify potential therapeutic interventions. The recent findings indicate that modulating bile acid metabolism could provide a new avenue for treating liver diseases, including liver cancer.
Can enhancing FXR function help patients with liver cancer?
Yes, enhancing FXR function may be beneficial for patients with liver cancer. Research indicates that activating FXR can counteract the adverse effects of bile acid imbalance caused by the dysregulation of the YAP FXR pathway. By promoting bile acid homeostasis, therapies that stimulate FXR could potentially reduce liver damage and lower the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
What recent advances have been made in understanding bile acid imbalance and liver cancer?
Recent advances include the identification of a critical molecular switch in the regulation of bile acids linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies, particularly those led by Yingzi Yang at Harvard, revealed that the YAP FXR pathway is a key player in this imbalance. This new insight opens doors for potential liver cancer treatments that target FXR activation and regulate bile acid excretion.
Is there a connection between liver disease research and the development of bile acid therapies?
Yes, liver disease research is increasingly focusing on bile acids as key targets for therapy. The understanding of how bile acids influence health, particularly through pathways like YAP FXR, is leading to novel approaches in treating liver conditions, including hepatocellular carcinoma. These insights could pave the way for the development of bile acid-based therapies that restore homeostasis and mitigate disease progression.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Acid Imbalance | Imbalances in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, notably hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. |
| Molecular Switch | A key molecular switch has been identified that regulates bile acid production, which may influence potential treatment for liver cancer. |
| YAP and FXR Interaction | YAP, a protein involved in cell growth regulation, represses FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), crucial for bile acid homeostasis. This results in bile acid overproduction and liver damage. |
| Potential Treatment Implications | Targeting YAP’s function or enhancing FXR activity may provide new treatment avenues for liver cancer, halting the cycle of bile acid overproduction. |
Summary
Bile acid imbalance related to liver cancer is a significant health concern, as emerging research uncovers the mechanisms leading to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruption in bile acid production not only contributes to liver injury but also illuminates potential therapeutic strategies. By understanding the interaction between YAP and FXR, scientists are hopeful that new pharmacological solutions targeting these pathways can reduce liver damage and potentially prevent the progression of liver cancer.