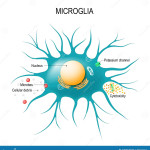
TIM-3 Alzheimer’s Therapy is emerging as a groundbreaking approach in the fight against Alzheimer’s disease, leveraging the mechanisms of the immune system to combat cognitive decline. This innovative therapy centers around the TIM-3 molecule, which is known to inhibit brain immune cells, particularly microglia, from clearing harmful plaques from the brain. Recent studies have demonstrated that by targeting TIM-3, researchers can enhance microglia function, leading to improved cognition and memory retrieval in animal models. The promise of this Alzheimer’s treatment lies not just in plaque reduction, but also in the restoration of cognitive abilities, resurrecting hope for millions afflicted by this relentless disease. As ongoing research delves deeper into the complexities of microglia and their role in neurodegeneration, TIM-3 Alzheimer’s Therapy stands at the forefront of a potential paradigm shift in how we approach Alzheimer’s therapy.
The exploration of TIM-3 Alzheimer’s Therapy represents a significant advancement in neurodegenerative disease management, utilizing immune system insights to address cognitive issues associated with Alzheimer’s. At the heart of this therapeutic strategy is the TIM-3 checkpoint molecule, which modulates the activity of brain immune cells, specifically microglia, crucial in maintaining a healthy neural environment. By dismantling the inhibitory effects of TIM-3, scientists aim to revitalize microglia function and enhance the brain’s ability to eliminate amyloid plaques, paving the way for meaningful Alzheimer’s treatment. As researchers continue to uncover the intricacies of this immune response, the potential for cognition improvement and memory enhancement offers a novel pathway in Alzheimer’s research and therapy development. This approach not only proposes a way to tackle the physical components of Alzheimer’s but also addresses the emotional and cognitive burden the disease imposes on patients and families alike.
Introduction to TIM-3 and Its Role in Alzheimer’s Therapy
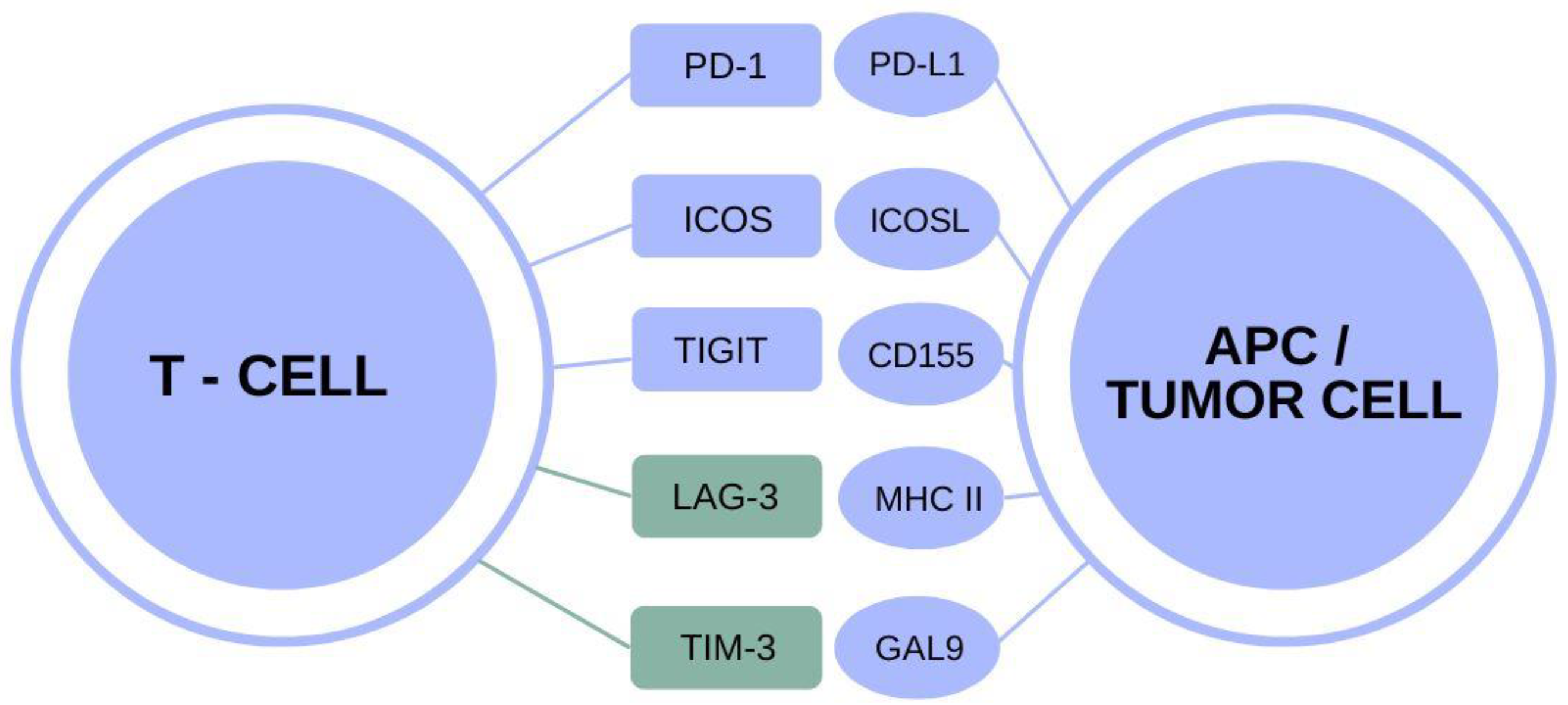
The TIM-3 molecule has emerged as a critical player in the landscape of neurodegenerative diseases, particularly Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Research has illuminated its inhibitory role within the brain’s immune response. By studying the functional dynamics of TIM-3, scientists hope to unlock new pathways for intervening in cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s. This potential for TIM-3 therapeutic strategies reflects a shift towards targeting immune mechanisms to enhance cognitive function and memory recovery.
Notably, TIM-3’s function resembles that seen in cancer therapies, where checkpoint inhibitors have been pivotal in reactivating immune responses against tumors. Similarly, by inhibiting TIM-3, researchers aim to restore the ability of brain immune cells, particularly microglia, to clear amyloid plaques, which are symptomatic of Alzheimer’s. This approach is not only innovative but offers a promising avenue of research that aligns with the emerging understanding of Alzheimer’s as an autoimmune-like condition.
Mechanisms of Microglial Function in the Brain
Microglia are the resident immune cells of the brain, uniquely tasked with maintaining homeostasis and responding to pathological changes. In the context of Alzheimer’s disease, the microglial cells become hindered in their normal functions due to the expression of TIM-3. Typically, these cells engage in synaptic pruning during development and clearance of harmful debris in later life, but the overexpression of TIM-3 inhibits this essential function, leading to plaque accumulation and subsequent cognitive impairment.
The implications of TIM-3 on microglial phagocytosis are profound. By understanding the genetic factors that influence TIM-3 expression, scientists can explore targeted therapies that promote the reactivation of these brain immune cells. This can potentially reverse the detrimental build-up of amyloid plaques and restore cognitive abilities, confirming the necessity for continued investigation into TIM-3 modulation as a therapeutic target.
Exploring the Relationship Between TIM-3 and Cognitive Improvement
Cognitive improvement in Alzheimer’s patients hinges on the effective clearance of neurotoxic amyloid plaques, which TIM-3 has been shown to inhibit. The recent findings from experiments involving genetically modified mice lacking the TIM-3 gene have provided exciting insights. In these models, microglial activity was enhanced, allowing for more effective plaque clearance and a noticeable restoration of cognitive function. This breakthrough suggests that TIM-3 antagonism could lead to significant memory recovery in individuals suffering from Alzheimer’s.
The recovery observed in memory tests among the TIM-3 knockout mice, who demonstrated improved navigation skills within mazes, underlines the potential viability of TIM-3 as a target in human therapies. By mimicking the conditions of these successful experiments, researchers aim to develop treatments that could yield similar improvements in Alzheimer’s patients, ultimately paving the way for new interventions that directly enhance cognitive resilience.
Antibody-Based TIM-3 Therapies in Alzheimer’s Treatment
The development of TIM-3 antibody therapies represents a promising frontier in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Such therapies would aim to inhibit the TIM-3 mediated checkpoint on microglia, helping to restore their ability to clear accumulated plaques. This approach differentiates itself from traditional Alzheimer’s treatments by leveraging the immune system’s intrinsic capabilities rather than solely targeting amyloid or tau proteins.
Emerging studies suggest that existing anti-TIM-3 antibodies, initially developed for cancer immunotherapy, could be repurposed for Alzheimer’s treatment. This dual application not only accelerates the research and development process but also enhances the hope for better therapeutic outcomes in AD. By systematically validating anti-TIM-3 therapies in clinical trials, the medical community could usher in a new era of Alzheimer’s treatment focused on harnessing the brain’s immune architecture.
Genetic Factors and TIM-3 Expression in Alzheimer’s
The genetic landscape surrounding Alzheimer’s disease is complex, but the TIM-3 molecule has been identified as a significant contributor to late-onset forms of the illness. Specific polymorphisms in the TIM-3 gene (HAVCR2) are associated with an elevated risk of developing Alzheimer’s, affecting its expression levels and, consequently, the functionality of microglial cells. Understanding these genetic relationships provides a basis for personalized approaches to treatment, potentially tailoring interventions based on an individual’s genetic predisposition.
By focusing on the genetic mechanisms that regulate TIM-3 expression, researchers can identify bio-markers for Alzheimer’s risk and progression. This insight will inform more nuanced treatment strategies that not only address existing symptoms but also target the underlying genetic factors contributing to the disease. Such advancements are essential for developing effective, individualized therapies.
Neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s Disease
Neuroinflammation plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, with microglia often being the first responders to pathological changes in the brain. In the presence of amyloid plaques, however, the expression of TIM-3 causes microglia to transition to a state of unresponsiveness, failing to mount an effective immune response. Consequently, the brain succumbs to chronic inflammation and toxicity, exacerbating neurodegeneration.
Strategies aimed at modulating neuroinflammation by targeting TIM-3 could potentially reverse this detrimental cycle. By restoring microglial activity and enhancing their ability to clear amyloid plaques, new therapies can mitigate inflammation-driven cognitive decline, ultimately improving overall brain health and cognitive function in Alzheimer’s patients.
Potential Implications of TIM-3 Research
The discovery of TIM-3’s impact on Alzheimer’s opens a myriad of possibilities for therapeutic interventions. With the potential to repurpose established antibodies, the research underscores the need for further exploration into immune system strategies in neurodegenerative disorders. If successful, this could redefine the therapeutic landscape of Alzheimer’s, moving beyond symptomatic relief to potential disease-modifying treatments.
Moreover, the insights gained from TIM-3 research will likely fuel advancements in related fields, encouraging a broader understanding of immune responses in the brain. This work could catalyze innovative approaches to other neurodegenerative diseases, solidifying the role of immune modulation as a cornerstone of future therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing cognitive health.
Future Directions in Alzheimer’s Research
As research progresses, the future of Alzheimer’s therapies may be significantly influenced by ongoing studies into TIM-3 and other immune checkpoint molecules. Researchers are currently investigating how to effectively apply TIM-3 inhibitors in human clinical trials, aiming to validate findings observed in preclinical models. If TIM-3 modulation proves effective in restoring cognitive function in Alzheimer’s patients, it could lead to groundbreaking treatment paradigms that prioritize immune system engagement.
Moreover, the combination of TIM-3 therapies with existing Alzheimer’s treatments could yield a synergistic effect, enhancing overall efficacy. Future studies must also focus on long-term outcomes and safety profiles, ensuring that any new therapies promote cognitive improvements without undesirable side effects.
Concluding Thoughts on TIM-3 and Alzheimer’s Treatment
The journey towards a better understanding of TIM-3’s role in Alzheimer’s disease underscores the complexity of brain health and immune interactions. As research delves deeper into the mechanisms of microglial activity and immune modulation, the potential for innovative therapies continues to grow. TIM-3 offers a promising avenue for restoring cognitive function, representing a shift towards harnessing the body’s intrinsic immune response in combating Alzheimer’s.
As scientists work tirelessly to translate these findings into clinical applications, the hope is that TIM-3 targeted therapies will not only halt the progression of Alzheimer’s but may ultimately pave the way for a cure. Emphasizing collaborative efforts and inter-disciplinary research will be key in advancing this exciting frontier of Alzheimer’s treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does TIM-3 play in Alzheimer’s treatment?
TIM-3 is an immune checkpoint molecule that inhibits brain immune cells called microglia. In Alzheimer’s treatment, targeting TIM-3 can enhance the microglia’s ability to clear amyloid plaques, potentially improving cognitive function.
How does the TIM-3 molecule affect microglia function in Alzheimer’s disease?
In Alzheimer’s disease, the TIM-3 molecule prevents microglia from engulfing harmful amyloid plaques. By inhibiting TIM-3, researchers aim to restore the microglial function, allowing these immune cells to clear plaques and enhance cognition.
Can TIM-3 inhibitors improve cognition in Alzheimer’s patients?
Yes, TIM-3 inhibitors have shown promise in preclinical studies by enhancing the clearance of plaques in mice models, leading to improvements in memory and cognition. This suggests a potential for developing Alzheimer’s therapies targeting TIM-3.
What findings support the use of TIM-3 in Alzheimer’s therapy?
Recent studies indicate that deleting the TIM-3 gene leads to more effective clearance of plaques by microglia in Alzheimer’s models, resulting in cognitive improvements. This highlights TIM-3’s critical role as a target for Alzheimer’s therapy.
What implications does high TIM-3 expression have for Alzheimer’s disease?
High expression of TIM-3 on microglia in Alzheimer’s patients correlates with impaired plaque clearance, contributing to cognitive decline. Consequently, TIM-3 represents a potential therapeutic target to enhance microglial activity and improve brain health in Alzheimer’s.
What potential therapies are being developed around TIM-3 for Alzheimer’s treatment?
Therapies may involve anti-TIM-3 antibodies or small molecules that block TIM-3’s inhibitory effects on microglia, thus promoting plaque clearance and cognitive enhancement in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
How does the deletion of TIM-3 in mouse models affect Alzheimer’s pathology?
In genetically modified mice lacking TIM-3, microglia showed increased activity in clearing amyloid plaques, leading to reduced plaque burden and noticeable improvements in cognitive behaviors, such as remembering and navigating mazes.
What are the next steps in researching TIM-3 for Alzheimer’s disease?
The next steps include testing human anti-TIM-3 antibodies in mouse models equipped with the human TIM-3 gene, which aims to assess the therapeutic potential of blocking TIM-3 in combating Alzheimer’s plaque accumulation.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| TIM-3 Alzheimer’s Therapy | A new approach leveraging TIM-3, which is linked to late-onset Alzheimer’s, may enhance cognition by allowing microglia to clear brain plaques. |
| Research Findings | The study demonstrated that deleting TIM-3 increased plaque clearance and improved memory in mice. |
| Microglia Function | Microglia are brain immune cells that prune synapses but can become dysfunctional with age due to TIM-3. |
| Potential Treatment | Anti-TIM-3 therapies could be developed to target Alzheimer’s without the adverse effects seen with anti-amyloid antibodies. |
Summary
TIM-3 Alzheimer’s Therapy offers a promising new direction for combating Alzheimer’s disease by leveraging advances in immunology. The recent findings indicate that targeting TIM-3 can empower brain immune cells to eliminate dangerous plaques and improve cognitive functions in mice suffering from Alzheimer’s. With the majority of Alzheimer’s cases being late-onset, further research into TIM-3 inhibitors may lead to innovative treatments that could significantly enhance the quality of life for millions of individuals affected by this debilitating condition. Continuing studies aim to evaluate the effectiveness of TIM-3 therapies in human models, potentially revolutionizing the approach to Alzheimer’s care.