Is sugar addictive? This provocative question stirs a good deal of debate in nutrition circles, as many grapple with understanding sugar addiction and its implications on our health. Research indicates that sugar can trigger cravings similar to those seen in addictive substances, leading to compulsive eating and strong desires for sweet foods. The health effects of sugar can be significant, influencing everything from mood to metabolism, thus raising concerns about excessive sugar consumption. For those looking to understand how to navigate their health, sugar consumption guidelines recommend limiting added sugars, as doing so can help minimize sugar cravings and promote better overall wellbeing.
When discussing the allure of sugary foods, one might wonder about the phenomenon often referred to as sweet cravings or sweet tooth. This craving for sugar is not solely about taste; it’s a complex interplay of biological and psychological factors that can lead some individuals to develop unhealthy eating habits. Many people find that their diets are saturated with sweeteners, leading to a cycle of dependence reminiscent of substance dependencies, although the exact classification remains uncertain. Terms like sugary substance dependency and compulsive sweet consumption frequently arise in discussions about dietary habits and health effects linked to sugar. Ultimately, understanding these dynamics is crucial in managing one’s dietary intake and making informed decisions for a healthier lifestyle.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a controversial topic, as many people experience intense cravings and compulsive eating behaviors around sugary foods. While researchers acknowledge that sugar can stimulate pleasure receptors in the brain, which leads to a feeling of reward similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Some experts believe that the accessibility and high palatability of ultra-processed foods contribute significantly to these cravings. The challenge arises from cultural norms that promote high sugar consumption, often overwhelming an individual’s ability to moderate their intake.
It is essential to recognize that while sugar might exhibit some addictive-like qualities, the effects of sugar in moderation can differ drastically from those of drugs classified as addictive. When consuming sugar as part of a balanced diet—including fruits, vegetables, and grains—individuals are less likely to experience negative health effects associated with excessive sugar consumption. Awareness of sugar intake is crucial, as seen with guidelines from organizations like the American Heart Association, which recommend limits on added sugar intake to promote overall health.
The Effects of Sugar on Our Health
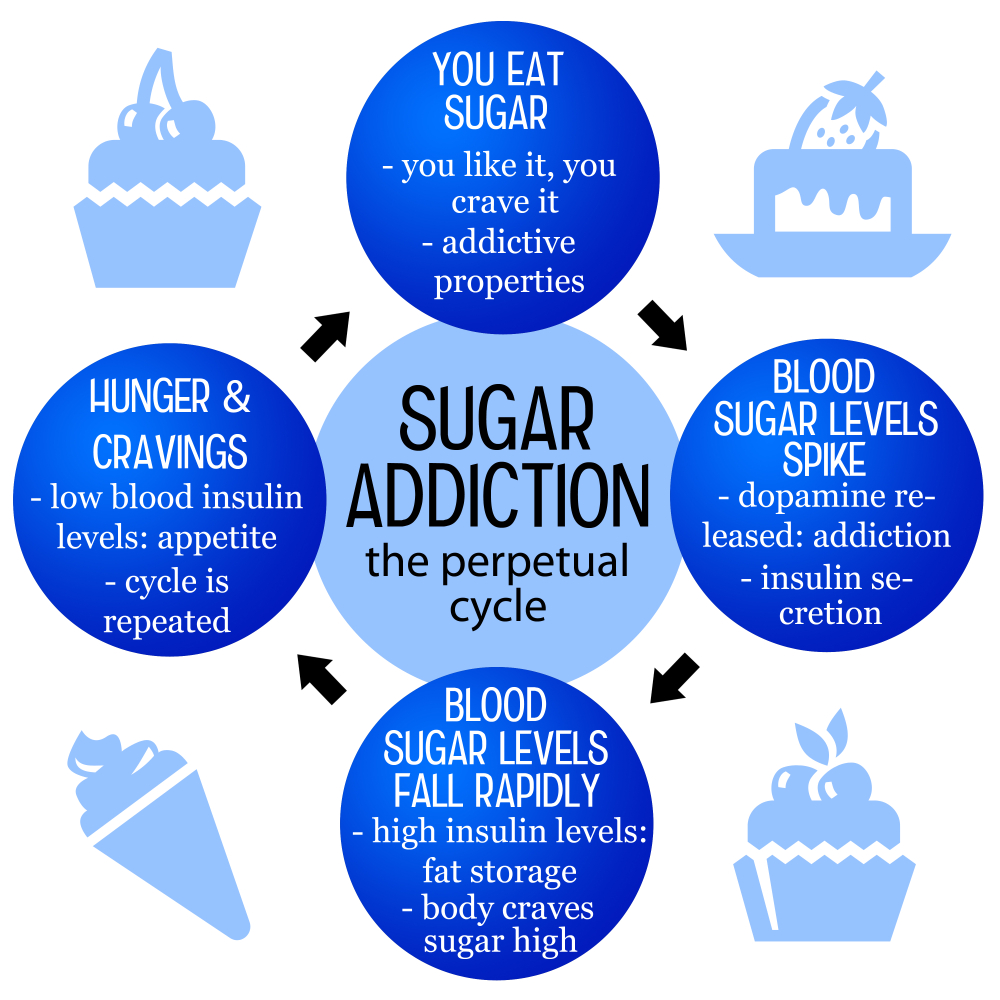
Excessive sugar consumption has been linked to numerous health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. The addictive qualities of sugar can lead to a cycle of cravings, resulting in even more sugar being consumed. This upward spiral not only impacts physical health but can also affect psychological wellness, making individuals feel trapped in their habits. Understanding the health effects of sugar can motivate individuals to seek healthier alternatives and strategies to reduce their sugar intake.
Moreover, sugar’s impact on health goes beyond just weight gain; it can lead to inflammation and insulin resistance, both of which are predisposing factors for various diseases. Moderating sugar consumption is important, and adhering to established guidelines can help mitigate these health risks. Individuals are encouraged to read food labels carefully, recognizing hidden sugars in processed foods, to make more informed dietary choices. A balanced approach to consuming sugar—recognizing its role in our diets without overindulging—is essential for maintaining optimal health.
Strategies to Reduce Sugar Cravings
To manage sugar cravings effectively, it’s essential to adopt gradual changes rather than attempting to cut sugar out entirely. Going ‘cold turkey’ can often lead to withdrawal-like symptoms, including headaches and anxiety, which may set individuals back in their journey toward healthier eating. Instead, one can begin by identifying high-sugar foods in their diet and finding healthier alternatives that satisfy cravings without excess sugar. For instance, replacing sugary snacks with fruits or yogurt can help reduce overall sugar intake while still providing a degree of sweetness.
Additionally, understanding triggers for sugar cravings can be beneficial in reducing consumption. Emotional eating is a common response to stress or sadness, making it crucial to address the underlying emotions rather than turning to sugary comfort foods. Mindfulness practices, like meditation or journaling, can provide insights into one’s relationship with food and promote healthier coping mechanisms. Ultimately, building a sustainable and enjoyable approach to eating—rich in whole foods while observing moderation with sugar—is vital for long-term health.
Sugar Consumption Guidelines for a Healthier Life
As mentioned previously, adhering to official sugar consumption guidelines can significantly improve health outcomes. The American Heart Association advises that men limit added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons, and women to 6 teaspoons, with even lower limits for children. These guidelines serve as a framework to help individuals make conscious decisions regarding their sugar intake, promoting overall well-being. Monitoring portions and being aware of added sugars in processed foods can facilitate these goals.
One effective strategy is to educate oneself about the various names for sugar that appear on food labels, such as high fructose corn syrup, sucrose, and agave nectar, among others. This knowledge can empower consumers to make healthier choices and reduce reliance on added sugars in their diets. As people begin to understand their consumption patterns and make conscientious changes, they can cultivate healthier eating habits that not only support physical health but also enhance mental and emotional well-being.
Navigating the Social Landscape of Sugar Consumption
Navigating social occasions often proves challenging for individuals trying to reduce sugar intake, especially in environments where sugary treats are prevalent. Celebrations, gatherings, and even work functions typically feature high-sugar foods, making it easy to drift away from health goals. Communicating preferences with friends and family can help mitigate pressure to indulge in sweets. Additionally, individuals can contribute alternatives, such as fruit platters or healthier desserts, to ensure there are enjoyable options that align with their dietary goals.
Creating a supportive community is instrumental in managing sugar consumption effectively. Sharing experiences and strategies with others can provide encouragement and accountability, making it easier to adhere to personal health goals. Establishing habits such as exercise and meal prepping in a group setting not only enhances motivation but also makes the process enjoyable. By fostering an environment that prioritizes health, individuals are more likely to maintain their commitment to reducing sugar intake while enjoying social interactions.
Exploring the Psychological Effects of Sugar
Research has increasingly indicated that sugar may affect mental health. The immediate pleasure derived from consuming sugar can lead to a temporary mood boost, but excessive sugar intake may also contribute to anxiety and depression in the long run. This paradox highlights the importance of moderation; while sugar can enhance pleasurable experiences, over-reliance on sweet foods can lead to negative emotional states. Understanding this psychological dynamic is vital for those looking to establish a healthy relationship with food.
Additionally, sugar cravings may also drive individuals into cyclical patterns of overeating and restriction, contributing to a disordered relationship with food. Addressing such issues often involves not just dietary changes but also seeking support from professionals who specialize in nutrition and mental health. These experts can provide strategies to combat the emotional triggers of cravings, helping individuals to approach sugar—and their diet in general—more mindfully, ultimately improving both mental and physical health.
Recognizing Hidden Sugars in Your Diet
Many people are unaware of just how much sugar is hidden in their everyday foods. Sauces, salad dressings, and even savory items can contain added sugars that contribute to the daily intake without any realization. This stealthy addition of sugar often leads to surpassing the recommended consumption limits, resulting in negative health effects. Being diligent in checking food labels and ingredients can empower individuals to take control of their sugar consumption and make healthier choices.
Moreover, educating oneself about common food categories that are often laden with added sugars—such as snacks, granola bars, and breakfast cereals—can assist in navigating better dietary decisions. By opting for whole, unprocessed foods, individuals can significantly reduce their hidden sugar intake, thereby making strides toward health improvement. The more informed a person is about what they consume, the easier it becomes to avoid excess sugar and its harmful effects, allowing for a healthier lifestyle overall.
The Role of Sugar in Modern Diets
In today’s food environment, sugar plays a central role in many diets around the world. As food manufacturers strive to create products that are highly palatable, sugar is often used to enhance flavors and improve consumer satisfaction. This reliance on sugar can lead to inadvertently high consumption levels, raising concerns about the potential health implications. Understanding where sugar fits into the modern diet is crucial for promoting healthier eating habits.
However, it is essential to acknowledge that sugar does have its place in a balanced diet when consumed responsibly. From providing energy to enhancing the enjoyment of food, sugar is not inherently bad. The key lies in awareness and moderation. Advocating for policies that limit added sugars in processed foods can help promote a healthier food supply, empowering consumers to make more informed choices while still enjoying the sweetness life has to offer.
The Importance of Moderation in Sugar Intake
Moderation is key when it comes to sugar intake, as overly restrictive diets can often backfire and lead to binge eating. Setting realistic goals for reducing sugar in the diet encourages sustainable change rather than drastic measures that are difficult to maintain. It is important to allow for the occasional indulgence to satisfy cravings, while balancing those moments with healthier choices. By creating a diet that celebrates moderation, individuals can enjoy sweets as part of a well-rounded eating plan.
Incorporating small changes, such as reducing portion sizes or choosing less sugary alternatives, can gradually lead to improved health outcomes without sacrificing enjoyment. This approach aids in fostering a healthy relationship with food, allowing individuals to savor their favorite treats without the guilt. By understanding the effects of sugar and making conscious decisions around its consumption, it’s possible to strike a balance that supports both health and happiness.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like other substances such as nicotine and alcohol?
While sugar does not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction like nicotine or alcohol, it can create cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. The psychological and physical effects of sugar consumption can mimic addiction, particularly when consumed in excess.
What are the health effects of sugar consumption?
Excess sugar consumption is linked to various health issues including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women to maintain better health.
How do sugar cravings develop in individuals?
Sugar cravings often develop due to the consumption of ultra-processed foods high in sugar, fat, and sodium. These foods are highly palatable and can lead to habitual consumption, making withdrawal difficult when one tries to cut back.
What sugar consumption guidelines should I follow?
To adhere to sugar consumption guidelines, it’s advisable to limit added sugars to no more than 9 teaspoons per day for men and 6 teaspoons for women. Reading food labels can help manage intake effectively.
Can quitting sugar lead to withdrawal symptoms?
Yes, when individuals reduce their sugar intake significantly, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, anxiety, and dizziness. These reactions, caused by the sudden decrease in sugar consumption, can vary in severity.
What is the difference between sugar addiction and other substance addictions?
The differences lie primarily in the severity of withdrawal symptoms and the classification of substances. While sugar can promote cravings similar to addictive substances, it is essential for survival, unlike drugs that can be completely eliminated from the diet.
Are there benefits to consuming sugar in moderation?
Yes, consuming sugar in moderation is beneficial as it enhances flavor and texture in food. It is necessary to maintain a balanced diet, as sugar is naturally found in fruits, vegetables, and other essential food groups.
How can I manage my sugar cravings effectively?
To manage sugar cravings, gradually reduce sugar intake rather than quitting cold turkey. Incorporating more whole foods and being mindful of added sugars in processed foods can help lessen cravings.
What types of sugar should I focus on avoiding?
Focus on avoiding added sugars typically found in sugary beverages, snacks, and processed foods. Natural sugars found in whole fruits and dairy are less concerning when consumed in moderation.
Is it possible to classify sugar as an addictive substance?
While sugar exhibits some qualities associated with addiction, it is not classified as an addictive substance officially. Its unique role in our diets makes it different from regulated drugs like nicotine and alcohol.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, but it can cause cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. |
| The modern food system is filled with ultra-processed foods high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, increasing cravings. |
| When people abruptly stop consuming high-sugar foods, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms (headaches, anxiety), but these are less severe than those from addictive drugs. |
| Sugar has some beneficial qualities and is needed in moderate amounts for flavor and texture in food. |
| The average American consumes 20 teaspoons of added sugar per day; recommended limits are 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women. |
| Gradually reducing added sugar intake is recommended over abruptly eliminating it. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The debate surrounding sugar’s addictive nature continues, as while it does lead to cravings and some withdrawal symptoms, it lacks the stringent clinical classification of true addictions like alcohol or nicotine. The need for sugar in our diets suggests moderation rather than elimination, making it essential to understand the balance of intake to maintain both enjoyment and health.