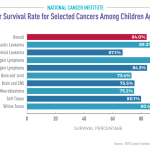
U.S. biomedical innovation has long been at the forefront of medical breakthroughs, forging a path for significant advancements in healthcare and technology. This dynamic ecosystem thrives on a robust collaboration between public-private research partnerships, which have transformed the landscape of biomedical research since World War II. The impact of government support and federal funding for research during this pivotal period cannot be overstated; it laid the groundwork for innovations like the mass production of penicillin that saved countless lives. However, recent discussions about NIH funding cuts have raised concerns about the sustainability of these critical funding sources. As the world looks to the U.S. model for inspiration, understanding the history of biomedical innovation becomes essential to navigate current challenges and secure future advancements.
The landscape of biomedical advancement in the United States is characterized by a rich tapestry of collaboration and innovation. Often referred to as a model for global health progress, this ecosystem has thrived due to the integration of government resources and academic research efforts, especially in light of wartime demands. The influence of federal investment in research initiatives has proven invaluable, particularly in moments of urgency, such as those witnessed during the Second World War. While the ongoing debate surrounding federal funding for research poses challenges, the historical context reveals a clear narrative of resilience and success. Such a profoundly interconnected system has not only forged a history of breakthroughs but continues to shape the future of medicine and health.
The Role of Federal Funding in U.S. Biomedical Innovation
Federal funding has been a cornerstone of the U.S. biomedical innovation ecosystem, facilitating advancements that have not only impacted medicine but have also driven economic growth. Historically, significant investments from federal agencies, particularly the National Institutes of Health (NIH), have provided the financial backing necessary for pioneering research and development. This funding has catalyzed collaborations between universities and private industries, leading to breakthroughs like vaccines and new therapies, showcasing how essential public financial support is to scientific progress.
The scrutiny surrounding federal funding calls attention to the delicate balance between supporting innovation and managing budget constraints. With proposals to cap reimbursements for indirect research costs, experts warn that such cuts could stifle the growth of biomedical research. Reductions in NIH funding, particularly in an era focused on combating significant health challenges, could hinder the continuation of a partnership that has historically laid the foundation for transformational medical advancements.
Public-Private Research Partnerships: A Model for Innovation
Public-private research partnerships have emerged as an effective model for fostering innovation in the biomedical sector. These collaborations leverage the strengths of both the government and private entities, combining governmental resources with the agility and expertise found in the private sector. The success of such initiatives was significantly demonstrated during World War II, when government-backed research programs propelled advancements in medical technologies and treatments that proved pivotal in addressing urgent wartime health challenges.
By pooling resources and knowledge, public-private partnerships can drive forward technology and therapeutic innovations at an accelerated pace. For instance, the rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines stands as a recent example where such collaborations maximized efficiencies in research and distribution. As the scrutiny over federal funding grows, understanding the dynamics of these partnerships is crucial for maintaining a healthy ecosystem that fosters scientific advancements.
The Impact of World War II on Biomedical Research
World War II played a transformative role in shaping the landscape of biomedical research in the United States. The urgent need for medical solutions to protect soldiers in the field triggered substantial government investment in scientific research, yielding groundbreaking advancements such as mass-production techniques for antibiotics like penicillin. This concerted effort not only addressed immediate military health needs but also laid the groundwork for civilian medical practices that would evolve in the decades to follow.
The establishment of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) facilitated a systematic approach to wartime research, enabling faster deployment of innovative solutions to pressing healthcare challenges. The legacies of this era can be seen in the structured research frameworks established, which continue to influence U.S. biomedical research approaches today. The collaborative spirit born from wartime demands has also fostered an environment where scientific inquiry thrives, reinforcing the historical significance of the marriage between public funding and academic research.
The Evolution of the NIH and Its Role in Innovation
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has evolved significantly since its inception, transforming into a fundamental pillar of the U.S. biomedical innovation ecosystem. Initially characterized by limited funding and a narrow scope, the NIH expanded its mission post-World War II, focusing on advancing medical research through extramural funding. This expansion enabled universities and research institutions to pursue innovative projects that have led to pivotal discoveries and health advancements in the ensuing decades.
Continuation of robust NIH funding is paramount for sustaining the momentum of biomedical research. Recent discussions about potential budget cuts raise concerns among researchers about the future of essential public health programs and advancements. The NIH’s legacy as a driving force behind numerous breakthroughs is threatened if proper funding mechanisms are not protected, emphasizing the need for a stable financing model that fuels ongoing innovation.
Understanding the Historical Context of Biomedical Innovation
The history of biomedical innovation in the U.S. reflects a rich tapestry woven through strategic investments and collaborations that have defined modern medicine. Beginning in earnest during World War II, federal initiatives led to unprecedented advancements in medical technology and pharmaceuticals. This era not only showcased the urgent need for effective health solutions but also highlighted the role of strategic partnerships in advancing medical science.
Post-war, the relationship between government, academia, and private industry deepened, creating an interconnected web of innovation that continues to thrive today. Key historical moments serve as a reminder of the achievements made possible through collaboration, setting the stage for contemporary research endeavors and emphasizing that understanding the roots of biomedical innovation is crucial for fostering ongoing development in the field.
The Legacy of WWII Research on Current Biomedical Challenges
The research conducted during World War II has left a lasting legacy on contemporary biomedical challenges. As scientists addressed the pressing health concerns of the time, such as controlling infectious diseases like tuberculosis and malaria, they laid the groundwork for methodologies and technologies still in use today. The innovations that emerged not only contributed to military health but also significantly enhanced public health strategies in subsequent years.
Today, as the world faces a myriad of health crises, from pandemics to chronic diseases, the lessons learned from WWII research are invaluable. The emphasis placed on rapid innovation and adaptive research infrastructures can inform current strategies, ensuring that science remains agile and responsive to the ever-evolving landscape of public health.
Navigating NIH Funding Cuts: The Future of Innovation
The potential cuts to NIH funding present a critical juncture for the future of biomedical innovation. With growing pressure on federal budgets, the threat of reduced funding has raised alarms among researchers who depend on these resources for their work. Such cuts could disrupt vital projects and stymie medical advancements, emphasizing the importance of advocating for robust funding mechanisms that support the research ecosystem.
Addressing NIH funding cuts requires a multifaceted approach, including a reevaluation of how public funding is allocated and the impact it has on long-term innovation. As the scientific community rallies against these proposed reductions, it is imperative to highlight the return on investment that federal funding brings—not only in terms of health improvements but also in enhancing U.S. leadership in global biomedical research.
The Future of U.S. Biomedical Innovation
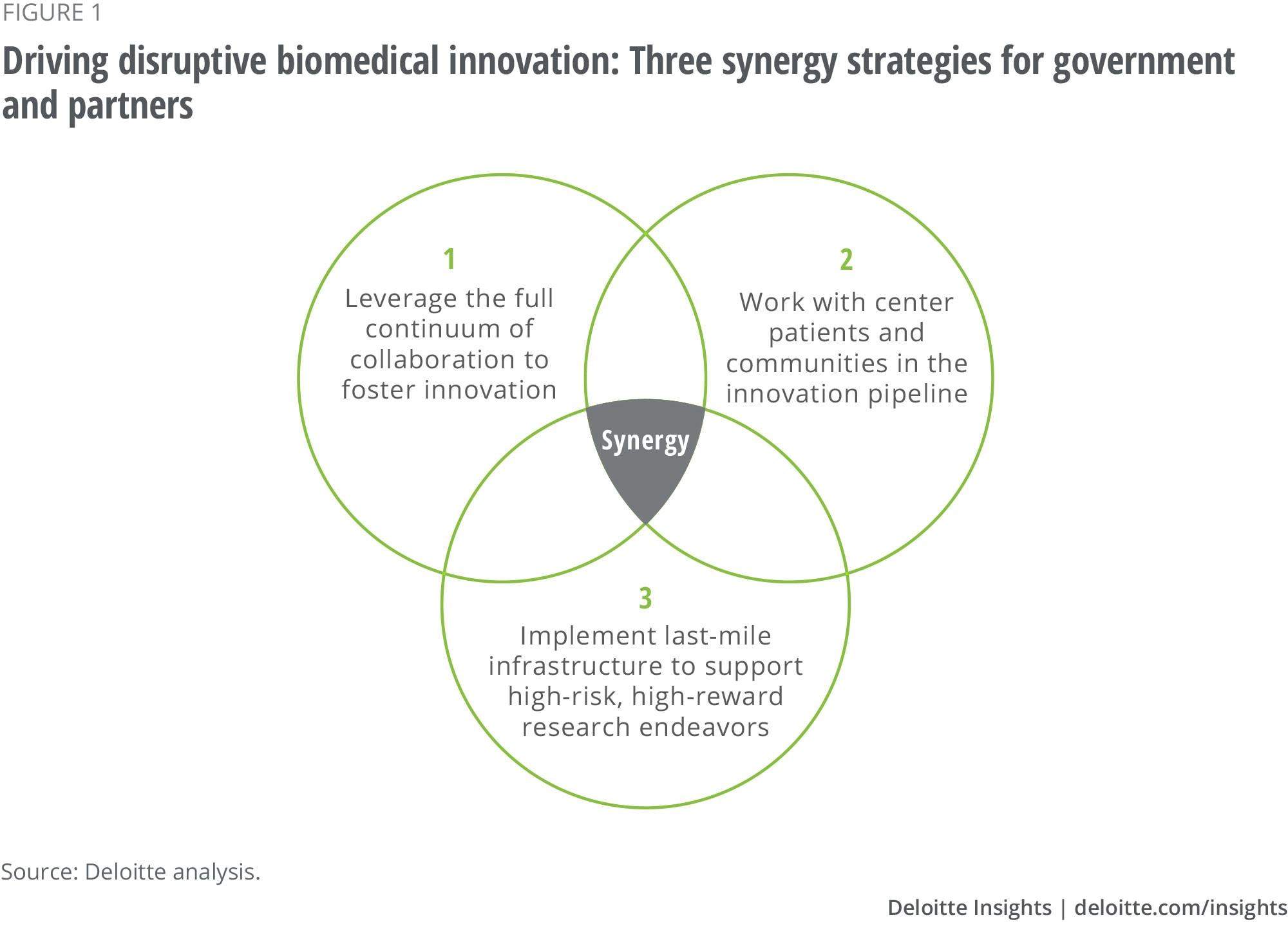
Looking ahead, U.S. biomedical innovation stands on the brink of unprecedented opportunities and challenges. The landscape of healthcare is rapidly evolving, with emerging technologies like gene therapy and personalized medicine leading the charge. As we integrate advanced research tools and methodologies, maintaining strong public-private partnerships will be crucial in driving these innovations forward.
Moreover, navigating the complexities of regulatory environments while pursuing groundbreaking research will require collaboration at all levels—from government to academia to industry. Ensuring that funding remains robust and responsive to the needs of researchers will position the U.S. as a steadfast leader in the global biomedical innovation arena.
Preserving America’s Leadership in Biomedical Research
To preserve America’s leadership in biomedical research, it is essential to commit to the continued support of public-private partnerships and federal funding initiatives. A concerted effort to maintain and boost investment in research is critical to sustaining the legacy of innovation that has defined the U.S. biomedical landscape. Policymakers and stakeholders must recognize the importance of these partnerships in driving scientific and technological progress.
The collaborative approach that underpins the U.S. innovation ecosystem has proven successful in global benchmarks. Ensuring that this framework remains intact will not only benefit American public health but also position U.S. researchers as leaders on the international stage in tackling global health challenges. Investing in this ecosystem is key to fostering a culture of innovation that will yield transformative medical advancements for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role did public-private research partnerships play in U.S. biomedical innovation during World War II?
Public-private research partnerships were fundamental to U.S. biomedical innovation during World War II, as they mobilized scientists from academia and industry to solve urgent health challenges. This collaboration, initiated by the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), led to significant breakthroughs, such as the mass production of penicillin, which drastically reduced disease impact on military personnel, showcasing the effectiveness of joint efforts in advancing medical research.
How did federal funding shape the landscape of U.S. biomedical innovation?
Federal funding has been crucial in shaping U.S. biomedical innovation by providing financial support for academic and clinical research. Agencies like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have historically funded transformative studies and projects, facilitating advancements in medical technology and public health. However, recent discussions about potential funding cuts could jeopardize ongoing research efforts and the robust partnership between government and research institutions.
What is the history behind the growth of U.S. biomedical innovation post-World War II?
The history of U.S. biomedical innovation post-World War II is rooted in the advancements achieved during the war, which laid a solid foundation for future scientific progress. The partnership between federal agencies, universities, and private industry transformed the biomedical field, leading to the establishment of strong research infrastructures and increased investment in drug development, ultimately giving rise to a golden age of pharmaceuticals.
What impact did government-supported research during World War II have on future U.S. biomedical innovations?
Government-supported research during World War II propelled future U.S. biomedical innovations by establishing a collaborative framework between federal entities and scientific communities. The urgent health needs during the war prompted the creation of new research methods and funding mechanisms, which fostered ongoing developments in medical science, exemplified by the postwar rise of antibiotics and other critical healthcare treatments.
How are NIH funding cuts likely to affect U.S. biomedical innovation?
NIH funding cuts could significantly impair U.S. biomedical innovation by reducing financial support for crucial research projects. These cuts may hinder the ability of research institutions to conduct important studies, limiting the progress of medical breakthroughs and compromising the longstanding public-private research partnerships that have been essential for advancing health technologies in the U.S.
What lessons can be learned from the historical context of U.S. biomedical innovation in relation to public-private partnerships?
The historical context of U.S. biomedical innovation underscores the importance of public-private partnerships in fostering scientific advancement. It highlights how collaborative efforts can address urgent health needs, mobilize resources effectively, and drive technological progress, serving as a model for future initiatives aimed at tackling contemporary healthcare challenges.
What were the effects of World War II on the evolution of the NIH and its funding for biomedical research?
World War II catalyzed the evolution of the NIH, expanding its role from a small, primarily intramural agency to a major funder of extramural research. This growth was essential for supporting biomedical research that emerged from collaborative efforts during the war, setting a precedent for the NIH’s significant influence on the field of medicine and public health in subsequent decades.
How has the U.S. biomedical innovation ecosystem become a model for other countries?
The U.S. biomedical innovation ecosystem has become a model for other countries due to its successful integration of public-private research partnerships, substantial federal funding, and a strong emphasis on research and development. This framework has fostered innovation, improved healthcare outcomes, and sustained economic growth, making it a benchmark for nations looking to enhance their own biomedical research capabilities.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The U.S. biomedical innovation ecosystem started during World War II, leveraging government-supported research to mass-produce penicillin. |
| Federal funding historically supports academic research, bolstering private sector development in medicine and technology. |
| The partnership between federal government and academia that emerged during WWII remains crucial to U.S. technological advancement. |
| The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has evolved significantly since the 1940s, now playing a pivotal role in biomedical research funding. |
| Innovations during WWII addressed urgent health issues among soldiers, reducing infectious disease-related casualties by up to 100%. |
| The antibiotic revolution of the 1950s and 1960s stemmed from research and medical advancements initiated by the wartime effort. |
| The U.S. model of public-private partnership is admired globally and has been a key driver of economic growth and healthcare improvements. |
Summary
U.S. biomedical innovation has emerged as a model for the world, rooted in a rich history of collaboration between the government and academic institutions that began during World War II. This partnership led to significant advancements in medical research and technologies, ultimately transforming healthcare and boosting economic growth. As federal funding continues to play a critical role in fostering innovation, it is imperative to uphold this successful framework to sustain the vitality of the U.S. biomedical sector.