Pediatric cancer recurrence presents a significant challenge for families confronting childhood cancer, particularly with types such as pediatric glioma. Recent advancements utilizing AI in medicine are transforming the landscape of brain tumor prediction, offering hope for improved recurrence risk assessment. A study from Mass General Brigham demonstrated that an AI tool could predict relapse risks in pediatric cancer patients with remarkable accuracy, far surpassing traditional methods. This innovative approach enables healthcare providers to better manage treatment plans for patients undergoing glioma treatment and enhances the overall quality of care. By understanding recurrence dynamics through AI-enhanced imaging analysis, families can prepare for potential outcomes with greater peace of mind.
Childhood cancer relapse is a pressing issue that affects pediatric patients and their families, especially in cases like brain tumors, particularly gliomas. The integration of artificial intelligence tools into the medical field is paving the way for more precise predictions regarding the risk of recurrence. The latest research highlights how AI can analyze changing data over time, significantly improving the prediction of when a patient might face a relapse. This forward-thinking approach not only aids in more effective glioma treatment but also refines the process of recurrence risk assessment, minimizing uncertainty and stress for young patients and their caregivers. Embracing such technological advancements could redefine pediatric oncology and its approach to managing and preventing relapses.
Understanding Pediatric Cancer Recurrence
Pediatric cancer recurrence, particularly in cases of gliomas, remains one of the most challenging aspects of childhood oncology. Although many pediatric gliomas can be treated effectively through surgical intervention, the potential for recurrence introduces a level of uncertainty and emotional turmoil for affected families. Studies indicate that while a significant number of cases achieve remission, there is still a considerable subset of patients who may experience a return of cancer after initial treatment. Understanding the dynamics of recurrence is crucial, as it not only impacts treatment strategies but also influences the psychological wellbeing of young patients and their families.
The advent of advanced predictive technologies, especially those utilizing AI, offers new hope for clinicians and families navigating the complexities of pediatric cancer recurrence. Traditional predictive models often fall short when it comes to accurately assessing the risk of relapse, leading to stress and anxiety during follow-up imaging. With a focus on minimizing psychological burdens on children, enhanced predictive tools can assist healthcare providers in identifying which patients may need more intensive monitoring and tailored treatment plans, effectively balancing vigilance with quality of life.
The Role of AI in Glioma Treatment
Artificial Intelligence has emerged as a revolutionary force in glioma treatment, significantly reshaping how predictions and assessments are conducted. Unlike conventional methods that rely on single snapshot imaging, AI technologies, especially those employing temporal learning, analyze a series of brain scans over time to derive more accurate insights regarding tumor behavior and recurrence risks. This shift not only enhances the precision of treatment strategies but also aligns with the broader movement towards personalized medicine in oncology.
AI’s ability to synthesize information from multiple scans allows for a comprehensive evaluation of tumor dynamics and patient-specific factors. By integrating historical imaging data, AI models can identify subtle changes that may indicate the onset of recurrence earlier than traditional methods would permit. As healthcare continues to evolve, embracing AI in glioma treatment means creating a more responsive and effective care paradigm, ensuring that pediatric patients receive timely interventions suited to their unique clinical profiles.
Assessing Recurrence Risk in Pediatric Patients
Risk assessment for recurrence in pediatric patients undergoing treatment for gliomas is a critical consideration in pediatric oncology. Traditional assessment approaches may offer a generalized view but lack the granularity needed for nuanced decision-making. With the integration of AI tools, healthcare practitioners can now evaluate recurrence risks with improved accuracy, thus facilitating more proactive treatment planning and monitoring. These assessments rely on comprehensive data sets, including genetic markers, imaging results, and clinical histories, to build a clearer picture of a patient’s prognostic outlook.
The implications of precise recurrence risk assessment extend beyond mere prediction; they influence the entire trajectory of patient care. For instance, identifying high-risk patients early can lead to more aggressive treatment protocols and monitoring, aimed at preemptively addressing potential relapses. This not only cultivates a more intensive approach to therapy but also helps in allocating healthcare resources where they are most needed, ultimately improving outcomes for vulnerable pediatric populations.
Longitudinal Imaging and Prediction Accuracy
One of the key findings in recent research is the importance of longitudinal imaging in enhancing prediction accuracy for pediatric cancer recurrence. AI systems utilizing temporal learning capitalize on this, allowing for a more robust analysis of how gliomas evolve over time. This approach dramatically improves the model’s ability to evaluate changes that may indicate a risk of recurrence, representing a significant shift from static imaging assessments. The predictive capability of these models can therefore guide clinical decisions with a higher degree of confidence.
Utilizing a series of images collected at different time points provides a richer dataset for interpretation, thereby increasing the model’s ability to detect patterns associated with tumor behavior. As these advanced AI tools gain traction, they pave the way for more sophisticated modeling in pediatric oncology, potentially leading to tailored treatment regimens that can mitigate the psychological and physical toll of prolonged monitoring and care for young cancer patients.
Future Directions in Pediatric Oncology
The integration of AI in pediatric oncology represents an exciting frontier, with significant implications for the treatment of gliomas and other childhood cancers. The potential to utilize AI-driven models for early detection and prediction of pediatric cancer recurrence could transform clinical practices and improve overall patient management strategies. As research continues to validate these technologies, practitioners are optimistic about the operational possibilities that lie ahead, potentially leading to innovations in patient care that are not just reactive, but proactive.
Future initiatives may further harness AI’s capabilities, driving innovations in personalized medicine to better serve pediatric populations. By refining tools that assess risk factors for recurrence and translating these insights into actionable treatment protocols, healthcare providers can foster an environment where childhood cancers are managed more effectively, reducing risks while enhancing the quality of life for young patients as they navigate their cancer journeys.
The Psychological Impact of Pediatric Cancer Care
Caring for pediatric cancer patients entails profound emotional and psychological challenges, not only for the children facing treatment but also for their families. The uncertainty surrounding cancer recurrence amplifies these stresses, leading to anxiety and fear that can linger long after the initial treatment has concluded. It is crucial for healthcare providers to address these psychological aspects while delivering medical care, as the emotional wellbeing of patients is closely tied to their treatment outcomes.
As AI continues to enhance predictive accuracy for recurrence, the hope is that this will reduce the frequency of unnecessarily burdensome imaging for low-risk patients, thereby alleviating some of the psychological stress associated with ongoing monitoring. Understanding that improved prediction tools can lead to a more tailored approach to follow-up care offers a dual benefit—reducing anxiety and enhancing the overall patient experience during a challenging time.
The Importance of Comprehensive Care Teams
The complexity of pediatric cancer treatment necessitates a holistic approach, where comprehensive care teams play a critical role in managing patient outcomes and experiences. By incorporating specialists from various fields—including oncology, surgery, radiology, and psychology—care teams can effectively assess the multifaceted needs of pediatric patients dealing with gliomas and potential relapses. Collaborative efforts ensure that all aspects of a patient’s health, including emotional and physical wellbeing, are prioritized.
AI tools that enhance risk assessment and prediction add another layer to the support provided by comprehensive care teams. With access to sophisticated predictive analyses, teams can formulate treatment plans that are not only evidence-based but also innovative, addressing individual patient factors and the likelihood of recurrence. This integrative model is vital for navigating the complexities of pediatric cancer care, ensuring that each child receives the best possible support tailored to their unique situation.
Patient and Family Education in Oncology
Education plays a pivotal role in pediatric oncology, particularly regarding understanding treatment options and the potential for cancer recurrence. Families often encounter overwhelming amounts of information, and having a clear understanding of how predictive tools, especially AI advancements, can affect treatment decisions is essential. Educating families about what to expect during the treatment process, including follow-up imaging and assessments of recurrence risk, helps to alleviate fears and allows for informed decision-making.
Furthermore, empowering families with knowledge about advancements in technology, especially the role of AI in patient outcomes, can foster a sense of agency in their care process. By promoting this understanding, healthcare providers can create a supportive environment where patients and their families feel confident in the treatment pathway ahead. This is particularly important in pediatric cases where emotional support and clear communication are paramount to navigating the journey through cancer treatment.
Advancements in Imaging Technology
The evolution of imaging technology has been instrumental in improving the diagnosis and monitoring of pediatric cancers, particularly gliomas. Sophisticated imaging modalities, combined with AI analytics, offer unprecedented capabilities for identifying embryonic tumor behavior, fostering better outcomes through improved early detection. The use of advanced imaging techniques allows for much greater detail in evaluating tumor progression and responses to treatment, greatly influencing recurrence predictions.
As these imaging technologies continue to advance, the integration of AI enhances their capabilities further. AI algorithms can process and analyze thousands of scans much more efficiently than human experts alone, identifying trends and anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed. This synergy not only supports clinical decision-making but also underscores the importance of continued research and development in imaging technology, ensuring better surveillance and management of pediatric cancer recurrences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is pediatric cancer recurrence and how does it relate to glioma treatment?
Pediatric cancer recurrence refers to the return of cancer after treatment, particularly in children diagnosed with various types of cancer, including pediatric gliomas. Gliomas are brain tumors that can be challenging to treat, and understanding their recurrence risk is crucial for optimizing treatment plans. Advances in AI-assisted imaging are now improving the ability to predict glioma recurrence, allowing for more tailored and effective treatment options.
How can AI in medicine improve the prediction of pediatric cancer recurrence?
AI in medicine enhances the prediction of pediatric cancer recurrence by analyzing multiple brain scans over time. This approach, known as temporal learning, enables AI algorithms to detect subtle changes in a patient’s imaging data that may indicate an increased risk of glioma recurrence. As a result, healthcare providers can better assess the likelihood of relapse and adjust treatment strategies accordingly.
What role does recurrence risk assessment play in the management of pediatric glioma?
Recurrence risk assessment is vital in managing pediatric glioma as it helps doctors identify which patients are likely to experience a relapse after initial treatment. By utilizing advanced AI tools to analyze longitudinal imaging data, clinicians can make informed decisions about monitoring frequency and potential adjuvant therapies, ultimately improving outcomes for young patients.
How effective is the AI tool developed for predicting pediatric cancer recurrence in glioma patients?
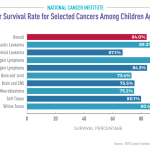
The AI tool developed for predicting pediatric cancer recurrence shows remarkable effectiveness, achieving an accuracy rate of 75-89% in forecasting the relapse of low- or high-grade gliomas within a year post-treatment. This performance is significantly better compared to traditional methods, which have an accuracy of only about 50%. Such advancements are critical for enhancing care across pediatric cancer treatment.
What are the implications of improved brain tumor prediction for pediatric cancer patients?
Improved brain tumor prediction through AI technology holds significant implications for pediatric cancer patients, particularly in managing gliomas. Enhanced accuracy in forecasting recurrence risks allows for more optimized follow-up protocols. Consequently, this may lead to reduced imaging frequency for low-risk patients and proactive treatment options for those at higher risk, ultimately improving overall patient care.
What challenges remain in utilizing AI for pediatric cancer recurrence predictions?
Despite promising results, challenges remain in validating AI models for pediatric cancer recurrence predictions in diverse clinical settings. Further research is essential to confirm the reliability and applicability of these models across various populations. Additionally, addressing the integration of these tools into existing clinical workflows is crucial for maximizing their potential benefits for pediatric glioma patients.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| AI Tool for Prediction | An AI tool outperformed traditional methods in predicting pediatric cancer relapse by analyzing brain scans over time. |
| Study Background | Conducted by researchers from Mass General Brigham and Boston Children’s Hospital, utilizing 4,000 MR scans from 715 pediatric patients. |
| Temporal Learning Technique | The AI model used temporal learning to analyze multiple scans taken over months to predict cancer recurrence. |
| Accuracy of Predictions | Found recurrence prediction accuracy between 75-89%, significantly higher than the 50% accuracy of single image assessments. |
| Clinical Application | Further validation is required before clinical trials and potential implementation in treating pediatric glioma patients. |
Summary
Pediatric cancer recurrence remains a critical concern as early prediction can significantly impact treatment outcomes. The recent study has revealed a promising AI tool capable of predicting the risk of relapse in pediatric cancer patients more effectively than traditional methods by analyzing multiple brain scans over time. This innovative approach not only improves accuracy but also aims to reduce the emotional and physical burden of frequent imaging on children and their families. Moving forward, the integration of AI in clinical settings could revolutionize how we monitor and treat pediatric cancer recurrence.